The Hindu summary of 6th January 2020 is given below Read it carefully you will get an attached pdf of notes along with it for Free :-
So the First News which is important for GS Paper IInd is :-

Basically we have to understand that why “Iraqi MPs vote to expel U.S. troops” so lets Go Back in 2001 When Al-qauida (organisation found by osama bin laden) Attacked USA in which more than 3000 civillians lost their lifes mostly known as The 9/11 Attack. so the US government ( G W Bush government) ask Afghanistan Taliban To hand-over Osama-bin-laden to US , Taliban Refused to hand-over Osama-bin-laden to US so Ultimately in October 2001 US attacked Afghanistan during this Attack G W Bush Also talked about “Axis of Evil ” it includes those countries those countries who are supporting terrorism , in possession of “WEAPONS OF MASS DESTRUCTION” and three countries made up of this axis:-
1) Iran 2) Iraq 3) North Korea
Iraq was alleged to be in possession of “WEAPONS OF MASS DESTRUCTION” so US and its Allies decided in 2003 that this is the time to launch a war against Iraq because Iraq was alleged to be in possession of “WEAPONS OF MASS DESTRUCTION” and Iraq is a threat to US and its Allies and Iraq was that time rulled by A Dictator “Saddam Hussein” Even before the war Saddam Hussein Allowed international Agency such as IAEA To Visit Iraq and check weather Iraq is in possession of “WEAPONS OF MASS DESTRUCTION” or not , but US and its Allies launched a war against Iraq Saddam Hussein Government was d-throned and saddam Hussein was caught alive and Hanged after the war was over no evidence of WMD was found in Iraq but this war transfer Iraq from a stable to Unstable country.
In 2009 the US President Barack Obama pulling the US troops from Iraq but then “Iraq gave birth to ISIS ” and to fight ISIS US troops decided to stay back in Iraq almost 5000 are thier in Iraq to support Iraq police to fight Against ISIS and because of the killing of “Qassem-saleimani” top millitary comandant of Iraq now As ISIS was defeated “Iraqi MPs vote to expel U.S. troops”
Another New from Page no:- 1 The Hindu 6th january 2020 Important for Prelims:-

As we know About Gaganyaan ( India’s first man mission to mars ) 4 Indian Airfrorce Pilots have been selected and sent to Russia for training but the question is why not in India so the Reason is We don’t have all the facilities which are required for this training but ISRO has proposed a Rs 2700 crore master plan to create top infrastructure so that in future we don’t require to send our people to outside for training and the place will be known as ” Human Space flight Centre (HSFC) ” located in karnatka.
Another New from Page no:- 8 The Hindu 6th january 2020 Important for (GS IInd Exam):-
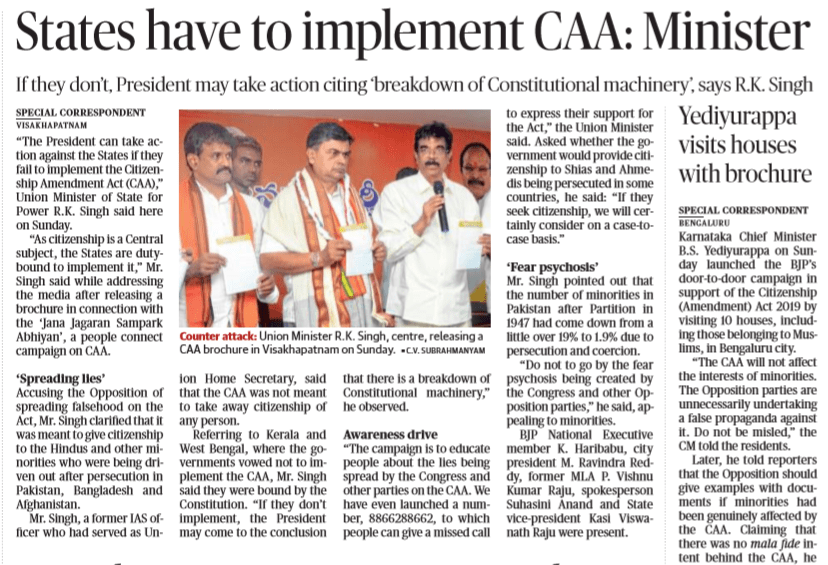
CAA has now become the Law of Land as it was passed by the parliament NPR ( National Population Register) has also been approved by union cabinet thier are several states which are catagorically stated that they are not going to impliment CAA like west bengal and kerala.
In above editorial the minster said that if any state does not impliment CAA than President rule under Article 356 will be imposed on them so the question is …. Is it Possible?
Lets take a look…….
There are two obligation on the part of the state:-
- Whenever a law is passed by the parliament it is the responsibility of the state to comply with those laws.
- It is the obligation on the part of the state government that whenever the central government is doing something exercising it executive functionality and if the state government is interfaring with the legitimate function of the centeral government than in both of these cases direction will be given by central government to state government.
And if then also the state government doesn’t follow the directions by central government than the President rule under Article 356 can be implimented.
Another New from Page no:- 9 The Hindu 6th january 2020 Important for (GS IIIrd Exam):-

Saras is India’s first indigenous light transport aircraft it is designed by a NAL national aerospace laboratories this NAL was established by the council for scientific and industrial research in the year 1959 can be important statement for your prelims exam initially it was headquartered in Delhi but in 1960 the headquarter was shifted to Bengaluru , NAL works closely with Hindustan aeronautics limited defence research and development organisation and Indian space organisation what is the prime responsibility of NAL the prime responsibility is developing civilian aircraft in India and NAL has developed in design SARAS which is India’s first light transport aircraft the first prototype of saras flu in the year 2004 later it was reported by newspapers that the project has been cancelled but in 2017 the project was revived now any NAL has told the parliamentary committee on science and technology that in order to give push to saras government should be the launch customer of these aircrafts that means the central government should buy at least 50 to 60 saras aircraft so that this project can become commercially viable and these aircraft can be used under udan scheme which is regional connectivity scheme of the Government of India please aircraft can also be used for VIP services as well that’s what you need to understand from this article.
Now we Look at the Editorial Column of The Hindu:-

First scoring a foreign policy self goal written by professor Jacob who teaches at JNU Delhi this is similar to the column written by Suhasini Haidar on January to 2020 in which the author says that the actions of the government on article 370 as well as on citizenship amendment act look like foreign policy self goals Mr Jacob argues when was the last time we had the mention of rising India when was the last time a foreign government tells back India’s permanent membership of United nation security council because now Indian diplomats are busy trying to explain to the world leaders trying to explain to the international powers why did we revoke the special status of Jammu and Kashmir why are the bringing about citizenship amendment at why are we trying to run out National register of citizens in this country Mr Jacob argues that if the objective of the government is that refugees from three countries who have been persecuted because of their religion if the objective of the government is to provide citizenship to the refugees then there was no need for citizenship amendment act in state the need was to have a refugee law in this country this refugee law should happen non-discriminatory as well because of all these decisions the author argues that India’s reputation has taken a hit we will lose our friends like Bangladesh and Afghanistan and that is why all are diplomats are busy in browsing the fires lit by these decisions of a government and that is why we are not in a position to decide whether we should join our CET or not what is going to be India’s role in Afghan peace process and weather India should join Japan and Australia in launching of front against China in Indian ocean region true that India can insert it’s diplomatic power in the neighbourhood that is what does newspaper column is all about.
Second Indian science Congress is India’s premier scientific organisation its headquarter is in Kolkata it was set up in the year 1914 the meetings of Indian science Congress are held annually in the first week of January can be an important statement for your prelims examination more than 30000 scientists who are the members of Indian science Congress and what is the objective of Indian science Congress to promote to advance because of science in India it’s not forget part 4A of the constitution talks about fundamental duties and one such fundamental duty is to promote scientific temper Indian science Congress has been at the centre of controversy for example last year a scientist say that covers work on using stem cell technology Andhra Pradesh University vice chancellor last year said that Ravan has 24 types of aircraft a professor from Tamil naidu say I hold degree in renewable energy when there is no such department as renewable energy in 2016 and Nobel laureate of Indian origin Venkatraman Ramakrishnan said I am not going to participate in Indian science Congress meetings since it is a circus there are people who say Indian science Congress is nothing but comedy for example of minister last year said that Stephen Hawking has accepted that there is that are mentioned in Vedas are superior than Einstein’s theory of relativity one member at the meeting of Indian science Congress last year said that Darwin’s theory of evolution is scientifically wrong express last year road that in India today stand up comedians say anything which is critical of a government for the members of the ruling party then they are arrested so Indian express road which means in India we take comedy too seriously and science today has now become comedy editorial also talks about it says that the science Congress needs new ideas and not the mix of myth and serial science what you need to understand from this editorial.
Those who will be appearing for civil services examination interview this can be a potential question asked by the panel in students for protesting against citizenship amendment act national register of citizens the assault on students at Jamia University the students took out protest matches and some of them also read the poem of Faiz Ahmed Faiz hum dekhenge when the students at IIT Kanpur read this poem of faculty at IIT Kanpur lodge the complaint and said this poem is anti Hindu it is also anti National committee was setup to prove whether this poem is Anti-national or anti Hindu although IIT Kanpur lecture on clarified that our committee is not going to investigate whether this poem is anti Hindu but it has generated a lot of controversy and let’s understand this newspaper column in slide detail Faiz Ahmed Faiz is one of the most renowned dhup rates is in the category of Mir taqi Mir Iqbal and Ghalib but faiz is also different from them is not like Ghalib been made because both of them were involved in romantic poetry Iqbal was more into religion his poetry represents more of Islamic philosophy but face was a revolutionary poet he wrote his famous poem mujhse pehli si Mohabbat mere Mehboob na maang Love you my target is a romantic poem but it is not in fact he wrote this poem when has read the communist manifesto written by Karl Marx and his friend Frederick Angels face was also against the division of the country on religious lines when general zia ul haq imposed martial law in Pakistan suspended the constitution of Pakistan has was highly critical of zia ul haq and here to spend some time in jail as well in 1979 Faiz Ahmed Faiz rote hum dekhenge lajim hai ki ham bhi dekhenge we shall see we are testing to see what was he talking about he was talking about social justice critics argue that in his poem hum dekhenge his talking about anal haq a nice talking about the role of the man of God that is why it is Islamic fundamentalism it is empty Hindu and that is why this form should be banned but the column is argues that when he writes on the lock and the rule of the man of God it is against zia ul haq because you want people to revolt against the Islamic fundamentalism of zia ul haq and ensure social justice in the society so this poem cannot be entirely Hindu cannot be Islamic fundamentalism care panneer selvam who is the readers editor of the Hindu he talks about his personal experiences in Nepal when in Nepal king and his mistake payment and imports absolute monarchy it was then that civil society activist journalist and writers the protested against the king by singing the terms of Faiz Ahmed Faiz and they were singing Faiz Ahmed Faiz most render to ham bol bol ke lab azaad Hain tere bol kaise hua ab tak Teri hai speak your lips are free speak your tongue is still yours and later on democracy was restored in Nepal so the writer says if else can help restored democracy in Nepal I can do so in India to you may agree or disagree with the writings of both of Columbus but that is what you need to understand from.
Hope you all Found This Blog helpful And please subscribe to our blog for daily updates…..








Reblogged this on Crack UPSC in First Attempt and commented: thank you